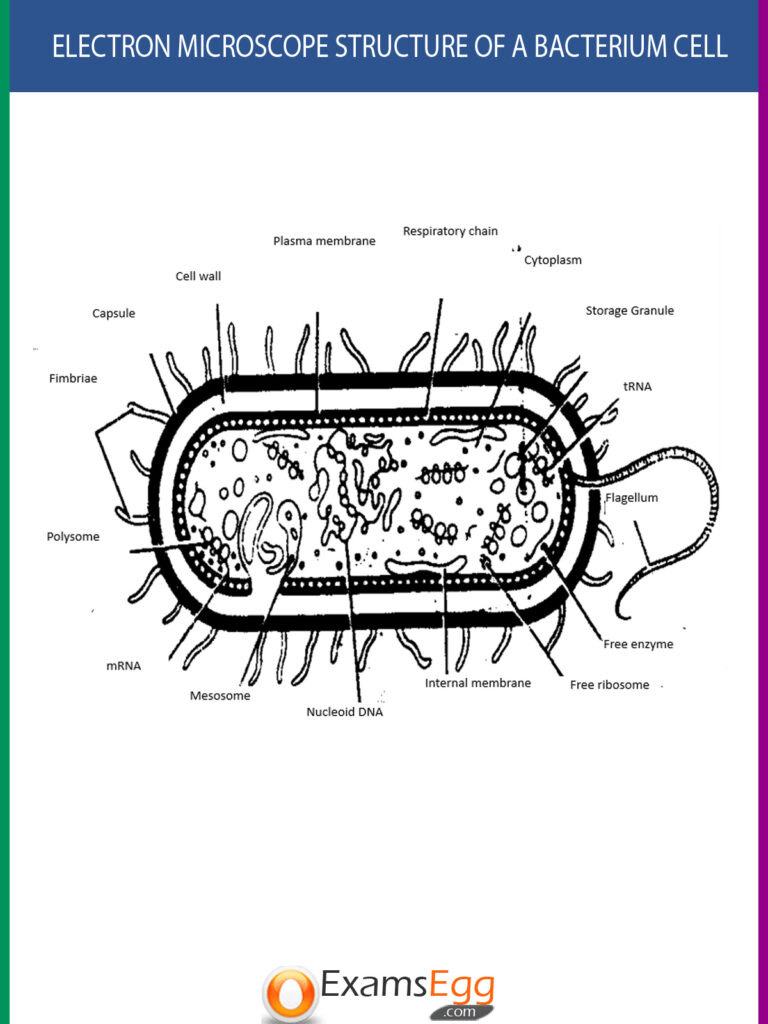
Bacteria can be destroyed by
(a) Dehydration
(b) Fermentation
(c) Oxidation
(d) Sterilization
The chief component of bacterial cell wall is
(a) Cellulose and chitin
(b) Cellulose and pectin
(c) Amino acids and polysaccharides
(d) Cellulose and carbohydrates
A substance that causes the disintegration of bacteria is
(a) Bacteriocin
(b) Bacterin
(c) Barophile
(d) Bacteriolysin
The hydrogen donor in bacterial photosynthesis is usually
(a) Water
(b) Hydrogen sulphide
(c) Sulphurus acid
(d) Ammonia
Bacteria present in food materials become inactive
(a) By washing food materials
(b) By keeping food materials at a temperature of 4° – 10°C
(c) By keeping food in polythene bags
(d) By keeping food materials in containers
Related: Hypertension quiz questions
Bacterial photosynthesis is very peculiar because it takes place
(a) Without CO2
(b) Without photosynthetic pigments
(c) Without light
(d) Without water
Which is not a cyanobacterium?
(a) Lyngbya
(b) Plectonema
(c) Anabaena
(d) Sinorhizobium
Which of the following is a way in which bacteria can develop resistance to antibiotics?
(a) Mutation
(b) Conjugation
(c) Both A and B
(d) Neither A nor B
One of the following is not applicable to Escherichia coli
(a) Transformation
(b) Transduction
(c) Flagella
(d) Diploid
What is the name of the process by which bacteria exchange genetic material?
(a) Conjugation
(b) Meiosis
(c) Mitosis
(d) Replication
What is a vector?
(a) Natural reservoir of disease
(b) Pathogenic bacteria
(c) Human parasite
(d) Organism carrying and transmitting disease causing micro-organism
Related: questions on Electromagnetic Waves
How many bacteria are produced in four hours if a bacterium divides once in half an hour?
(a) 8
(b) 64
(c) 16
(d) 256
Bacterial cells can be stained with
(a) Mercuric chloride
(b) Crystal violet
(c) Crystal violet and iodine
(d) Safranin
Which of the following is not a chemosynthetic bacteria?
(a) Nitrobacter
(b) Beggiatoa
(c) Azotobacter
(d) Nitrosomonas
Mesosome in a bacterial cell is
(a) Plasmid
(b) Connection between two cells
(c) Plasma membrane infolded for respiration
What is the shape of a bacillus bacteria?
(a) Round
(b) Spiral
(c) Rod-shaped
(d) Irregular
Related: Questions about Periodic Table with Answers
Why can the food be kept for a longer time in a cold house than in normal conditions?
(a) Insects can not enter
(b) Bacterial multiplication stops
(c) Bacterial multiplication is reduced
(d) There is plasmolysis at low temperature
Which of the following is an example of a disease caused by bacteria?
(a) AIDS
(b) Hepatitis B
(c) Malaria
(d) Tuberculosis
Penicillin inhibits bacterial multiplication because
(a) It checks spindle formation
(b) It destroys chromation
(c) It inhibits cell wall formation
(d) It checks RNA synthesis
What lives in the large human intestine and feeds on undigested food without harming the host?
(a) Predators
(b) Commensals
(c) Symbionts
(d) Parasites
Genes which confer antibiotic resistance on bacteria are located on
(a) Polysome
(b) Circular DNA molecule
(c) Plasmid
(d) RNA
Related: Questions on Relative Velocity
Which of the following is free-living aerobic non- photosynthetic nitrogen fixing bacterium?
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Azotobacter
(c) Nostoc
(d) Azospirillum
Which of the following is a beneficial function of bacteria in the human body?
(a) Digestion
(b) Respiration
(c) Sensation
(d) Reproduction
Sugary solution is changed to vinegar by the action of
(a) Azotobacter
(b) Diplococcus
(c) Bacillus subtilis
(d) Mycoderma aciti
Harmful poisonous substances secreted by Streptomyces and other soil saprophytic bacteria are
(a) Txoins
(b) Aflatoxin
(c) Antibiotics
(d) Antiseptics
The matrix around Nostoc colony is
(a) Gelatinous
(b) Hard and corky
(c) Cartilaginous
(d) No matrix at all
Related: Alkene Quiz
Which of the following is a type of bacteria?
(a) Fungi
(b) Virus
(c) Algae
(d) E. coli
Bacteria are included in which of the following kingdoms
(a) Protista
(b) Plantae
(c) Monera
(d) Animalia
The name cyanobacteria refers to
(a) Bacteria
(b) Blue-green algae
(c) Yeast
(d) Fungi
One of the useful activities of several bacteria is
(a) Nitrogen fixation
(b) Nitrification
(c) Operation of biogeochemical cycles
(d) All of the above
Related: Tongue Questions and Answers
‘The integration process’ in which a bacterial cell remain undestroyed and unaffected even in the presence of ‘phage’ is called as
(a) Plaques
(b) Virion
(c) Viroid
(d) Lysogeny
Gram negative bacteria differ from gram positive bacteria in that their cell wall is
(a) Thicker
(b) Without lipid
(c) Complex
(d) Simple
Which of the following does not evolve oxygen?
(a) Photosynthetic bacteria
(b) Blue-green algae
(c) Autotrophic plants
(d) Green algae
Mycoplasma differs from viruses in being sensitive to
(a) Sugar
(b) Tetracycline
(c) Protein
(d) Amino acid
Which of the following is a method of controlling bacterial growth?
(a) Antibiotics
(b) Vaccines
(c) Antifungal drugs
Related: Insects Quiz Questions and Answers
Typhoid fever is caused by
(a) Giardia
(b) Salmonella
(c) Shigella
(d) Escherichia
Which of the following does not evolve oxygen?
(a) Green algae
(b) Photosynthetic bacteria
(c) Autotrophic plants
Bacteria were for the first time observed by
(a) W.H. Stanley
(b) Louis Pasteur
(c) Anton Von Leeuwenhoek
(d) Robert Koch
Which of the following is bacterial disease?
(a) Measels
(b) Small pox
(c) Rabies
(d) Tuberculosis
Which of the following is a method of bacterial reproduction?
(a) Budding
(b) Binary fission
(c) Meiosis
(d) Mitosis
The poisonous substances commonly produced by bacteria are known as
(a) Toxin (Exotoxins)
(b) Auxins
(c) Antibiotic
(d) Antitoxins
Related: Light Polarization MCQ
Which of the following can cause food poisoning?
(a) Streptococcus
(b) Salmonella
(c) Staphylococcus
(d) E. coli
Mycoplasma is related to
(a) Algae
(b) Bacteriophage
(c) Virus
(d) L–form bacteria
Natural genetic engineer is
(a) Bacillus subtilis
(b) Pseudomonas sp.
(c) Escherichia coli
(d) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
What is the name of the protein structures on the surface of some bacteria that help them adhere to surfaces?
(a) Capsules
(b) Cilia
(c) Pili
(d) Flagella
The process of replication in plasmid DNA, other than initiation, is controlled by
(a) Plasmid gene
(b) Bacterial gene
(c) Cytoplasmic gene
(d) Mitochondrial gene